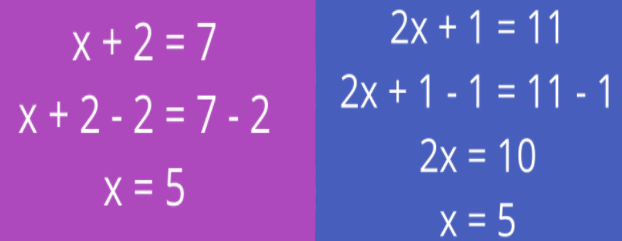Introduction to Algebra
A Persian Mathematician whose name was Muhammad ibn Musa Al-Khwarizmi (780-850 AD) is called the "Father Of Algebra. He wrote a book in the Arabic Language named Kitab Al Muhtasar fi Hisab Al Jabr-wal-Muqabala in 820 AD. Later on, it was translated into English named: The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing. This book gives a step-wise solution for Linear and Quadratic Equations. Furthermore, He described the methods of solving different and complex Mathematical problems.
The word ALGEBRA came from the Arabic word AL-Jabr which has its roots in a 9th-century codex written by Musa AL-Khwarizmi.
Algebra:
An Arabic word which means "Bringing together broken parts" is called Algebra. It is one of the useful tools of mathematics. It uses mathematical statements to describe the relationships between things that can vary with the time. Furthermore, It is not only a mathematical concept but also a skill for all of us because we mostly use it in our daily life without even recognizing it. Moreover, It is also useful in all other topics of mathematics. Now, You are going to study this topic in future in a very easy way.
Different Branches of Algebra:
There are different branches of Algebra that we are going to study now to find the values of two or more variables. These branches are
1. Elementary Algebra
2. Advanced Algebra
3. Abstract Algebra
4. Linear Algebra
5. Communicative Algebra
1. Elementary Algebra
The branch of Algebra that deals with the study of some basic operations, concept of variables, and simplification of an algebraic expression with its evaluation and linear equations having one or two variables.
What is Algebra?
A branch of mathematics that deals with mathematical symbols and the Arithmetic operations in utilizing these mathematical symbols are called Algebra.
Relationship between Algebra and Arithmetic:
- Faisalabad is in KPK. (False)
- Mango is a fruit. (true)
- Thank you (Neither true nor false)
- ▢ + 2 = 4
- ∆ is a beautiful city.
Algebraic Terms:
In order to write mathematical statements in algebra we use some basic terms which are given below:
- Coefficients
- Index or Exponential form
- Literals
- Constant
- Variables
Coefficients:
Literals:
The letters or Alphabets that are used in mathematics to represent an unknown quantity are called literals or literal numbers.
We use literals in math without assigning any specific value at all.
Example:
The formula for Area of a square is given below:
i.e. Area = l × b
Here, L and b are called literals.
Constant:
In mathematics, any number that have fixed value is called constant.
Example:
In x+3, the number 3 have fixed value is called constant.
Variables:
An unknown mathematical symbol which can take various numerical values and is not a constant, called variable.
Example:
In x+3, x is called a variable.